1、简介
rsync:remote sync:快速复制工具,复制的时候会比较源和目标的文件hash,如果源和目标文件的hash相同,则不会复制,只复制不同的内容。实现快速同步复制的目的,只同步目标文件没有的文件。
rsync不具备加密功能,但是传输文件快。但是scp具备加密功能,但是不快速,不会比对指纹信息
2、选项参数
rsync命令的工作模式
第一种:shell模式,也称作本地模式,操作和cp差不多,不通过网络来复制
第二种:远程shell模式,通过网络在不同主机之间传递,因为复制不加密,不太安全,此时可以利用ssh协议承载其数据传输过程,完成加密传输
第三种:列表模式,其工作方式与ls相似,仅列出源的内容:使用:-nv选项
第四种:服务器模式,此时,rsync可以工作在守护进程,随时能够接收客户端的数据请求;在使用时,可以在客户端使用rsync命令把文件发送到服务器端的守护进程,也可以向服务器请求获取文件到本地
四种工作模式,和scp的工作方式一样,命令,选项等都一样
Local: rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [DEST] Access via remote shell: Pull: rsync [OPTION...] [USER@]HOST:SRC... [DEST] Push: rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [USER@]HOST:DEST Access via rsync daemon: Pull: rsync [OPTION...] [USER@]HOST::SRC... [DEST] rsync [OPTION...] rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/SRC... [DEST] Push: rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [USER@]HOST::DEST rsync [OPTION...] SRC... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/DEST
rsync有许多选项:
-n:--dry-run,测试,在不确定命令是否能按照意愿执行时,务必要实现测试 -v:--verbose,详细输出模式 -q:--quiet,静默模式 -c:--checksum,开启校验功能,强行对文件传输进行校验 -r:--recursive,递归复制 -a: --archives.归档,保留文件的原有属性,属主属组权限等,等于-rlptgoD -p:--perms 保留文件的权限 选项:-rp等同于-a -t: --times 保留文件的内容修改时间戳 -l:--links 保留文件的符号链接,而不是复制链接指向的文件 -g:--group 保留文件的属组 -o:--owner 保留文件的属主 -D:--devices 保留设备文件 --delete 将无关的文件删除,a为同步的目标方,b为同步的源方,即使a,b都有文件c,后来b将c删除,默认情况下rsync不会删除c,除非加上这个参数, 同步的目标目录中有源目录中没有的文件A,会被删除,如果没有这个选项,文件A会保留 -e ssh:表示使用ssh协议作为继承 如果ssh的端口不是默认的22号端口,使用 -e 'ssh -p 2222' 来进行指定端口 -z:--compress或--compress-level=NUM 对文件压缩后传输 --progress:显示进度条 --stats:显示压缩的统计信息 --exclude=PATTERN 指定排除不需要传输的文件模式。 --include=PATTERN 指定不排除而需要传输的文件模式。 --bwlimit=100(限制为 100k Bytes/s)
scp的工作方式,rsync也是这样的
既可以将本地文件推送到对方,推
也可以将远程主机的文件拉取到本地,拉
也可以:client—-server方式,客户端可以推送文件到服务器端,也可以将服务器端的的文件拉取到本机
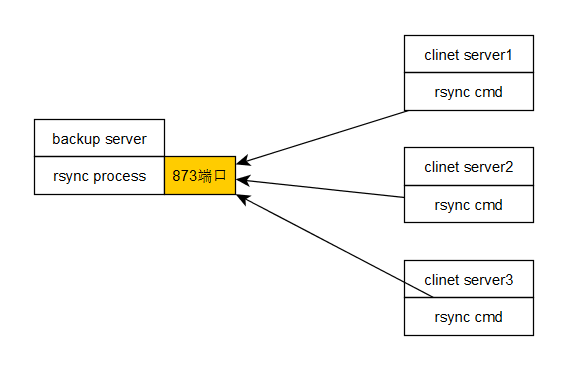
可以一台服务器作为备份服务器,上面运行rsync进程,然后有三台客户端服务器,每隔一段时间,将每个客户端服务器上面的资源推送到备份服务器上面
3、示例
注意:rsync命令使用中,如果源参数的末尾有斜线,只会复制指定目录的内容,而不复制目录本身。没有斜线,则会复制目录本身。包括目录
rsync -r /tmp/etc /tmp/test:会把目录etc直接同步至test目录中
rsync -r /tmp/etc/ /tmp/test:会把目录etc中的内容至test目录中
测试环境准备
[root@localhost /tmp]#rm -rf * [root@localhost /tmp]#ls [root@localhost /tmp]#mkdir etc test [root@localhost /tmp]#cp -r /etc/a[a-k]* ./etc #将/etc目录下面的一些文件复制过来测试 [root@localhost /tmp]#cd etc [root@localhost /tmp/etc]#ls abrt acpi adjtime akonadi
测试带/和不带/的区别
[root@localhost /tmp]#rsync -r etc test #同步的时候etc后面没有斜线 [root@localhost /tmp]#cd test/ [root@localhost /tmp/test]#ls #将整个目录复制同步过来了 etc [root@localhost /tmp/test]#cd etc/ [root@localhost /tmp/test/etc]#ls abrt acpi adjtime akonadi [root@localhost /tmp/test/etc]#cd .. [root@localhost /tmp/test]#ls etc [root@localhost /tmp/test]#rm -rf * #将文件删除继续测试 [root@localhost /tmp/test]#cd .. [root@localhost /tmp]#rsync -r etc/ test #同步的时候后面有斜线 [root@localhost /tmp]#cd test [root@localhost /tmp/test]#ls #将目录里面的文件同步过来了 abrt acpi adjtime akonadi
4、测试rsync命令和scp命令在禁止root登录的情况下,是否能够正常传输文件
结论:在禁止root登录的情况下,不管是输入密码还是公钥认证,rsync和scp均不能传输文件到对方机器上面
在允许root登录的情况下,在禁止GSSAPI和DNS的情况下,不管是输入密码还是公钥认证,rsync和scp均能传输文件到对方机器上面
在设置禁止root登录的情况下,要考虑更改后对这两个命令的影响,会导致文件传输异常
验证:正常情况下测试:sshd允许root登录,通过输入密码方式:两个都可以正常复制文件
主机:192.168.175.11 [root@localhost /tmp]#rsync -e ssh -r etc root@192.168.175.12:/tmp root@192.168.175.12's password: [root@localhost /tmp]#scp -r ./etc root@192.168.175.12:/tmp 完成
在输入密码的情况下,(12)机器设置:sshd服务设置:PermitRootLogin no,重载ssh服务:在(11)机器上面的rsync命令和scp命令都不能传输文件到对方机器上面(12)
[root@localhost /tmp]#rsync -e ssh -r etc root@192.168.175.12:/tmp root@192.168.175.12's password: Permission denied, please try again. root@192.168.175.12's password: Permission denied, please try again. [root@localhost /tmp]#scp -r ./etc root@192.168.175.12:/tmp root@192.168.175.12's password: Permission denied, please try again. root@192.168.175.12's password: Permission denied, please try again.
在已经通过公钥互信的情况下,(11)机器上面的生成的公钥已经传送到(12)机器上面,并且测试可以通过scp无密码传输文件,(12)机器设置:sshd服务设置:PermitRootLogin no,重载ssh服务:在(11)机器上面的rsync命令和scp命令都不能传输文件到对方机器上面(12)
在(12)机器上面设置可以root登录:PermitRootLogin yes,并且设置:GSSAPIAuthentication no,UseDNS no,重载sshd服务,将原有的公钥删除,通过rsync,scp都能传输文件到(12)机器上面,出现输入密码的界面很快,文件能够正常传输。当将公钥重新传送到(12)机器上面,使用rsync,scp都能传输文件到(12)机器上面,文件能够正常传输,而且速度很快。
5、rsync排除要同步的目录
下面是同步的源文件目录结构
[root@master ~]#tree . . └── file ├── a │ └── ab ├── b ├── c ├── d └── e └── eb 6 directories, 2 files
将家目录下的file目录同步到/tmp目录下面,同时排除目录d,e以及e的子文件
下面的正确,–exclude后面必须是相对路径,绝对路径是错误的。要排除的目录要单独一个一个指定
rsync -av --exclude d --exclude e /root/file /tmp
下面的错误,–exclude后面不能用绝对路径
rsync -av --exclude /root/file/d --exclude /root/file/e /root/file /tmp
还可以将要排除的文件列表放到一个文件里面,指定这个文件也可以,下面exclude.list 是一个文件,放置的位置是绝对路径的/tmp/exclude.list ,为了避免出问题,最好设置为绝对路径
但是里面要排除的文件列表一定要使用相对路径,可以使用通配符
[root@master /tmp]#cat exclude.list d e
然后使用下面的进行执行
rsync -av --exclude-from='/tmp/exclude.list' /root/file /tmp
6、配置rsync以daemon的方式运行
1、设定rsync服务器端:
安装超级守护进程 xinetd,因为rsync没有单独监听端口,是依靠xinetd来进行工作的
yum -y install xinetd rsync [root@localhost /etc/xinetd.d]#ll #会将rsync启动为服务进程 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 332 Mar 28 2014 rsync
为rsync提供配置文件,配置文件默认没有,要自己创建
配置文件为/etc/rsyncd.conf 如果需要知道配置文件的项目,帮助文档:#man rsyncd.conf
2、具体的配置,经测试,配置文件每行后面不能使用#来来注释
这里定义的是rsync的服务端的配置文件,一个全局配置和多个rsync共享配置 #Global Settings uid = nobody (设置运行进程的用户) gid = nobody use chroot = no(是否禁锢用户家目录) max connections = 10(服务器的最大连接数) strict modes = yes(是否完全检查权限等信息) pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log #Directory to be synced [synced_name] #同步的名字,以后就用这个名字 path = /path/to/some_dir ignore errors = yes(是否忽略错误) #同步时发生错误是继续还是终止 read only = no(只读) write only = no(只写) #如果只是备份数据,不允许其他拉取数据,则read为no,write为yes hosts allow = white_list_ip/net 白名单 hosts deny = black_list_ip/net 黑名单,*表示所有的 说明: 1.默认规则为允许访问,二者都不出现时 2.只出现hosts allow:定义白名单;但没有被匹配到的由默认规则处理,即为允许 3.只出现hosts deny:定义黑名单;出现在名单中的都被拒绝 4.二者同时出现,先检查hosts allow,如果匹配就allow,否则,检查hosts deny 如果匹配则拒绝,如二者均无匹配,则使用默认的,即允许 list = false 是否允许列出文件名单,不安全,就像网站的目录 uid = root(以哪个身份获取文件目录和内容) gid = root auth users = username (允许的用户,哪个ip上的哪个用户),将这个一行注释掉表示不使用认证方式 secrets file = /etc/rsyncd.passwd 用户密码的存放位置,将这个一行注释掉表示不使用认证方式
3、配置密码文件:/etc/rsyncd.passwd,明文存放,文件权限要设置为600,不然启动错误
username:password
4、配置服务能够启动,启动守护进程,最好将服务的开启启动也打开
修改/etc/xinetd.d/rsync文件,disable 改为 no
centos6 #chkconfig rsync on #service xinetd restart #ss -tnl 873/tcp listen centos7 #systemctl start rsyncd.service #ss -tnl 873/tcp listen
5、在客户端做测试,注意:要执行下面的同步操作命令,则服务器端必须要开启此服务进程,不然不能进行同步,在特殊的端口上面进行通信。阿里云就没有开,不能用rsync来进行同步yum源,好气呀(;′⌒`)),还好中国科大的源开了rsync,可以开心的同步源了~~~
Pull: rsync [OPTION...] [USER@]HOST::SRC... [DEST] rsync [OPTION...] rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/SRC... [DEST] #适用于rsync协议的类似于http格式的域名 Push: rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [USER@]HOST::DEST rsync [OPTION...] SRC... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/DEST
如果需要做周期性操作,定义crontab
rsync --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd install.log myuser@172.16.100.7::mydata
而且客户端本地应该提供密码文件,密码只需要包含指定的密码即可,不需要用户名;文件权限要设置为600,不然出错
7、测试
两台机器做测试:
192.168.175.11:做客户端
192.168.175.12:做服务端
测试系统:centos6.8,rsync为系统自带的rpm包
ssh-keygen -t rsa
ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.175.12
rsync -e ssh -r etc root@192.168.175.12:/tmp
在主机:192.168.175.12:设置sshd的配置文件,这样传输文件会跳过IP反解,速度快
[root@localhost /tmp]#sed -i 's@.*GSSAPIAuthentication.*@GSSAPIAuthentication no@' /etc/ssh/sshd_config [root@localhost /tmp]#sed -i 's@.*UseDNS.*@UseDNS no@' /etc/ssh/sshd_config [root@localhost /tmp]#service sshd reload Reloading sshd: [ OK ]
在主机:192.168.175.11上面做常规测试,不用ssh,即使不指定ssh,也会让输入ssh的密码,这里使用-a参数, 即使同步的文件里面有软链,也会同步过去,如果使用-r选项同步的话,遇到软链,会选择跳过不同步
注意:选项:-r会跳过一些非正常文件,比如软链接,但是选项:-a会将这些软链接文件也复制到目标目录中
[root@localhost /tmp]#rsync -a etc root@192.168.175.12:/tmp root@192.168.175.12's password:
在主机:192.168.175.11上面做常规测试,如果使用ssh进行同步数据,也需要输入ssh密码,正常全部同步成功
[root@localhost /tmp]#rsync -e ssh -a etc root@192.168.175.12:/tmp root@192.168.175.12's password:
测试发现同步确实非常快,节省带宽,加上–stats参数后可以看到每次同步的文件数量,即使目标的某个文件被重新touch一下,都能检测出来,并同步过去一个文件,只同步这一个文件
–
安装服务端软件
[root@localhost /tmp]#yi xinetd rsync
设置配置文件
[root@localhost ~]#cat /etc/rsyncd.conf #Global Settings uid = nobody gid = nobody use chroot = no max connections = 5 strict modes = yes pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log #Directory to be synced [mydata] path = /tmp/etc ignore errors = yes read only = no write only = no hosts allow = 192.168.175.11 hosts deny = * list = false uid = admin gid = admin auth users = admin1 secrets file = /etc/rsyncd.passwd
这里设置认证用户是admin1,但是实际在服务器端操作文件的是admin用户,这两个可以分开为不同的用户,admin1用户不用在服务器端系统上添加用户
因为上面设置的是通过admin用户来进行认证的,并且使用admin用户进行操作系统上的文件,因此要添加admin用户,并将/tmp/etc目录的属主设置为admin权限,不然用户没有权限写入
[root@localhost /tmp/etc]#useradd admin [root@localhost /tmp]#chown admin.admin etc/ [root@localhost /tmp]#ll total 4 drwxr-xr-x 7 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:31 etc
设置密码文件
[root@localhost ~]#cat /etc/rsyncd.passwd admin1:qwerty [root@localhost ~]#chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.passwd [root@localhost ~]#ll /etc/rsyncd.passwd -rw------- 1 root root 13 May 13 16:02 /etc/rsyncd.passwd
启动服务,最好将开机启动也打开
[root@localhost /tmp]#chkconfig rsync on #注意,必须启动,否则端口监听不起来 [root@localhost /tmp]#service xinetd restart Stopping xinetd: [ OK ] Starting xinetd: [ OK ] 查看873是否监听
在主机:192.168.175.11操作
将本地目录同步上去,因为mydata就表示:/tmp/etc目录,因此源目录后面要加/,同步后才能在:/tmp/etc下面看到文件
[root@localhost /tmp]#rsync -a etc/ admin1@192.168.175.12::mydata --stats Password: Number of files: 118 Number of files transferred: 1 Total file size: 24760 bytes Total transferred file size: 1512 bytes Literal data: 0 bytes Matched data: 1512 bytes File list size: 5587 File list generation time: 0.001 seconds File list transfer time: 0.000 seconds Total bytes sent: 5655 Total bytes received: 53 sent 5655 bytes received 53 bytes 1630.86 bytes/sec total size is 24760 speedup is 4.34
同步正常,这里的这些操作是和ssh没有关系的,即使ssh设置的是禁止root登录,依然可以同步成功
可以在客户端设置密码文件,这样同步数据就可以不使用交互式命令进行
在主机:192.168.175.11设置
[root@localhost /tmp]#cat /etc/rsyncd.passwd qwerty [root@localhost /tmp]#chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.passwd [root@localhost /tmp]#ll /etc/rsyncd.passwd -rw------- 1 root root 7 May 13 16:59 /etc/rsyncd.passwd
可以同步成功
[root@localhost /tmp]#rsync --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd -a etc/ admin1@192.168.175.12::mydata --stats Number of files: 118 Number of files transferred: 1 Total file size: 24760 bytes Total transferred file size: 1512 bytes Literal data: 1512 bytes Matched data: 0 bytes File list size: 5587 File list generation time: 0.001 seconds File list transfer time: 0.000 seconds Total bytes sent: 7162 Total bytes received: 38 sent 7162 bytes received 38 bytes 14400.00 bytes/sec total size is 24760 speedup is 3.44
在客户端:192.168.175.11操作
将远程服务器端的文件目录同步到客户端的/root目录下面
[root@localhost ~]#rsync --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd admin1@192.168.175.12::mydata ./ #默认如果要从服务器端拉取数据要指定哪个文件, skipping directory . [root@localhost ~]#rsync --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd admin1@192.168.175.12::mydata/* ./ #只将文件同步下来,目录没有同步下来 skipping directory alternatives skipping directory acpi skipping directory abrt skipping directory akonadi skipping directory alsa [root@localhost ~]#ls adjtime aliases aliases.db [root@localhost ~]#rm -rf * [root@localhost ~]#rsync --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd -a admin1@192.168.175.12::mydata ./ #两个文件都复制下来了 推荐这种复制方法,可以将软链接也复制下来 [root@localhost ~]#ll total 40 drwxr-xr-x 3 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:30 abrt drwxr-xr-x 4 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:30 acpi -rw-r--r-- 1 admin admin 46 May 13 15:31 adjtime drwxr-xr-x 2 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:31 akonadi -rw-r--r-- 1 admin admin 1512 May 13 15:31 aliases -rw-r--r-- 1 admin admin 12288 May 13 15:31 aliases.db drwxr-xr-x 2 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:31 alsa drwxr-xr-x 2 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:31 alternatives
8、注意
默认情况下服务端的文件都是只允许增加,不允许删除的,即某一时刻客户端文件和服务端文件同步完成后,两边的文件相同,但是当客户端将目录里面的一个文件:aliases 删除,同时增加一个文件:abc,然后将本地文件同步到服务器端,就会发现,只有abc增加到服务器端的目录了,但是aliases文件没有删除,这样是保险的措施,避免客户端误删数据,想找备份但是服务端也没有了
客户端
[root@localhost /tmp]#echo hello >> etc/abc [root@localhost /tmp]#rm -rf etc/aliases [root@localhost /tmp]#cd etc [root@localhost /tmp/etc]#ll total 40 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 May 13 17:24 abc drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 May 13 15:30 abrt drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 May 13 15:30 acpi -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 46 May 13 15:31 adjtime drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 13 15:31 akonadi -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12288 May 13 15:31 aliases.db drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 13 15:31 alsa drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 13 15:31 alternatives [root@localhost /tmp]#rsync --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd -a etc/ admin1@192.168.175.12::mydata --stats Number of files: 118 Number of files transferred: 1 #显示只同步了一个文件 Total file size: 23254 bytes Total transferred file size: 6 bytes Literal data: 6 bytes Matched data: 0 bytes File list size: 5588 File list generation time: 0.001 seconds File list transfer time: 0.000 seconds Total bytes sent: 5657 Total bytes received: 38 sent 5657 bytes received 38 bytes 11390.00 bytes/sec total size is 23254 speedup is 4.08
服务端
客户端删除的aliases文件还在,同时新增了文件
[root@localhost /tmp/etc]#ll total 44 -rw-r--r-- 1 admin admin 6 May 13 17:24 abc drwxr-xr-x 3 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:30 abrt drwxr-xr-x 4 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:30 acpi -rw-r--r-- 1 admin admin 46 May 13 15:31 adjtime drwxr-xr-x 2 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:31 akonadi -rw-r--r-- 1 admin admin 1512 May 13 15:31 aliases -rw-r--r-- 1 admin admin 12288 May 13 15:31 aliases.db drwxr-xr-x 2 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:31 alsa drwxr-xr-x 2 admin admin 4096 May 13 15:31 alternatives
如果想将服务端文件和客户端文件相同,即客户端删除的文件,服务端也删除,客户端同步的时候加上:–delete参数就可以实现
rsync在windows下同步文件
cwRsync我们可以去下面这个连接进行下载:https://www.itefix.net/cwrsync
下载解压后配置下,就可以正常使用,把目前cwRsync所在的路径加入到系统的环境变量中
/cygdrive/e/表示windows系统的E盘,/cygdrive/e/rsyncd.password表示E盘下的rsyncd.password文件。
rsync -avz –delete –progress /cygdrive/e /cygdrive/f
参考文档:https://www.ilanni.com/?p=8646
–
–
–
 江哥架构师笔记
江哥架构师笔记
评论前必须登录!
注册